Cre-GFP Adenovirus
Specifications
| SKU | 000023A |
| Name | Cre-GFP Adenovirus |
| Unit | 1.0 ml |
| Description |
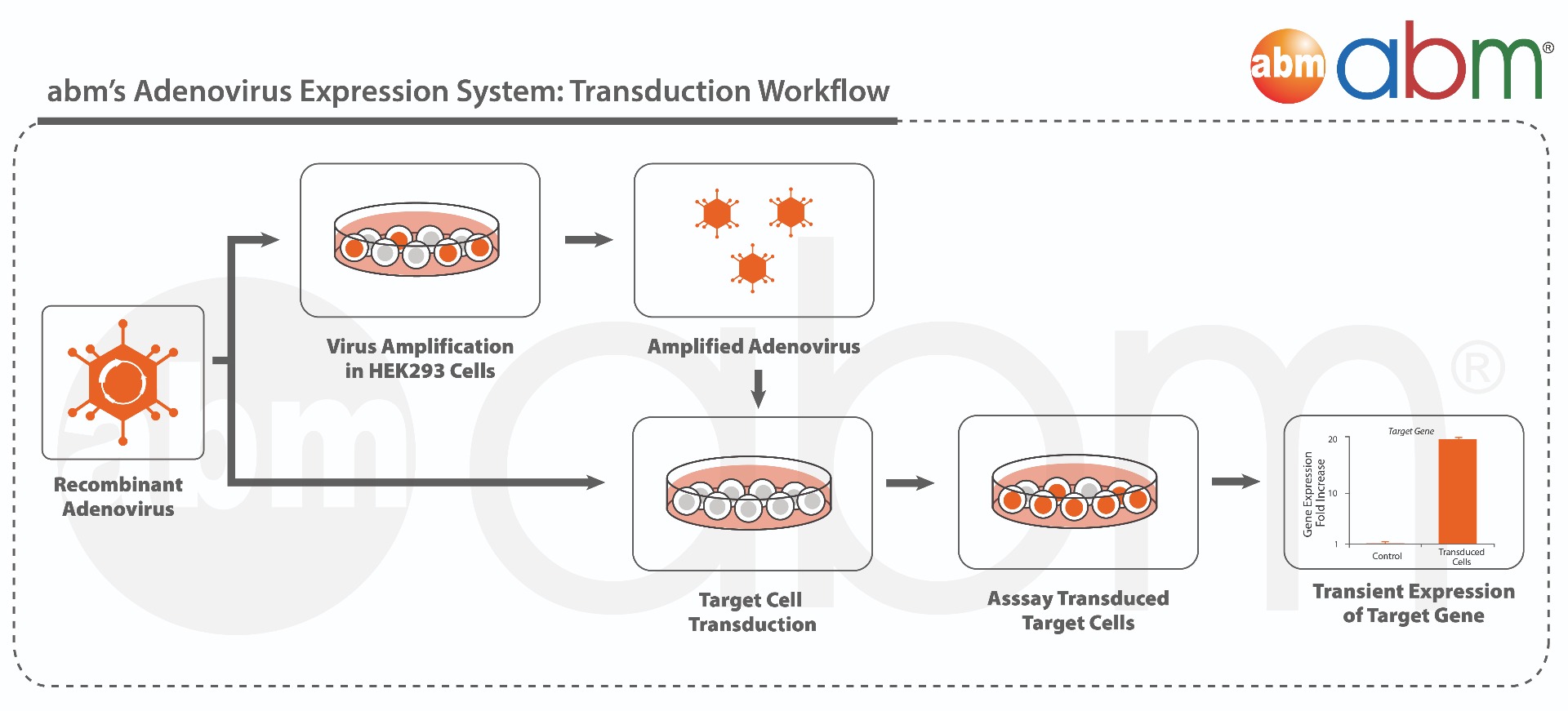
Cre Recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 Bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38kDa) is a member of the Integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the site specific recombination event between two DNA recognition sites (loxP sites). This 34 base pair (bp) loxP recognition site consists of two 13 bp palindromic sequences which flank an 8bp spacer region. The products of Cre-mediated recombination at loxP sites are dependent upon the location and relative orientation of the loxP sites. Two separate DNA species both containing loxP sites can undergo fusion as the result of Cre mediated recombination. DNA sequences found between two loxP sites are said to be "floxed". In this case the products of Cre mediated recombination depends upon the orientation of the loxP sites. DNA found between two loxP sites orienated in the same direction will be excised as a circular loop of DNA whilst intervening DNA between two loxP sites that are opposingly orientated will be inverted. The enzyme requires no additional cofactors (such as ATP) or accessory proteins for its function. This adenovirus constitutively expresses both Cre recombinase and GFP separately, each from a CMV promoter. This adenovirus is part of abm’s Adenoviral Expression System and can be used directly to transiently over-express your gene of interest in a wide range of host cells. This adenovirus can be used to amplify more adenovirus by transducing HEK293 cells. For enhanced transduction efficiency, the use of ViralEntry™ Transduction Enhancer (G515) at 1:100 is recommended at the time of transduction. |
| Applications |
|
| Storage Condition |
DMEM with 2% BSA & 2.5% Glycerol |
| Shipping Conditions |
High titer adenoviruses are shipped with dry ice and low titer adenoviruses are shipped with ice packs. For long term storage, it is recommended to store the viruses at -80°C in small aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Guarantee |
abm guarantees that the correct ORF construct is provided and the mRNA expression is displayed upon successful transduction. If this is not the case, we will provide a one-time replacement. Customers must provide adequate data to show >80% transfection efficiency with a positive control, plus additional qPCR data to evaluate the level of gene expression. The replacement will not be covered by the same guarantee. |
Documents
There are no Documents for this product yet!
FAQs
| Are your pPB protein expression vectors high or low copy number plasmids? | |
|
Our protein expression vectors are medium copy number plasmids and can be amplified using any standard miniprep or midi/maxi prep kits.
There is no standard protocol that fits all proteins, therefore recombinant protein expression will need to be optimized and determined experimentally.
|
| How long after transduction can the infection efficiency be observed? | |
|
You can observe transduction efficiency from 48 hours up to 5 days after infection.
|
| What are the primers to use for SV40T and SV40T tsA58 detection? | |
|
PCR primers:
SV40T Forward Primer Sequence
5’ AGCCTGTAGAACCAAACATT 3'
SV40T Reverse Primer Sequence
5’ CTGCTGACTCTCAACATTCT 3'
The two primers should amplify the region between 3677-4468bp, giving a 792bp fragment.
|
| What is the sequence of the SV40 large T antigen? | |
|
This information can be accessed on this page by clicking on "pLenti-SV40-T" under vector map. The Large T antigen is at position 5079-5927.
|
| When the protein is expressed from this vector, which enzyme do I need to use to remove my tag? | |
|
The enzyme required to remove the tag (if possible) will depend upon the vector backbone corresponding to your product:
1) pPB-C-His: the His tag is NOT cleavable.
2) pPB-His-GST: the His-GST tag can be cleaved using TEV protease.
3) pPB-His-MBP: the His-MBP tag can be cleaved using TEV protease.
4) pPB-N-His: the His tag can be cleaved with Thrombin.
5) pPM-C-HA: the HA tag is NOT cleavable.
6) pPM-C-His: the His tag is NOT cleavable.
7) pPM-N-D-C-HA: the N-terminal D-tag can be cleaved using TEV protease. The C-terminal HA tag is NOT cleavable.
8) pPM-N-D-C-His: the N-terminal D-tag can be cleaved using TEV protease. The C-terminal His tag is NOT cleavable.
Please see the following page for further details:
https://www.abmgood.com/Protein-Vector.html
|
| For G221 and LV620, what does the 'V12' in RasV12 mean? | |
|
The V12 means that amino acid # 12 is mutated from a Valine to a Glycine. Other than that, the sequence matches the coding region of HRAS perfectly (NM_005343).
|
| Where is the SV40T tsA58 gene sequence? | |
|
The SV40T tsA58 gene is located between 3138-5264bp, with the Alanine-to-Valine mutation at amino acid 438.
|
References
- Li, E., Wang, L., Wang, D., Chi, J., Smith, G. I., Klein, S., Cohen, P., & Rosen, E. D. (2022). Control of lipolysis by a population of oxytocinergic sympathetic neurons. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.27.509745
Controls and Related Product: