CRISPR Knockout Non-Viral Vector Library
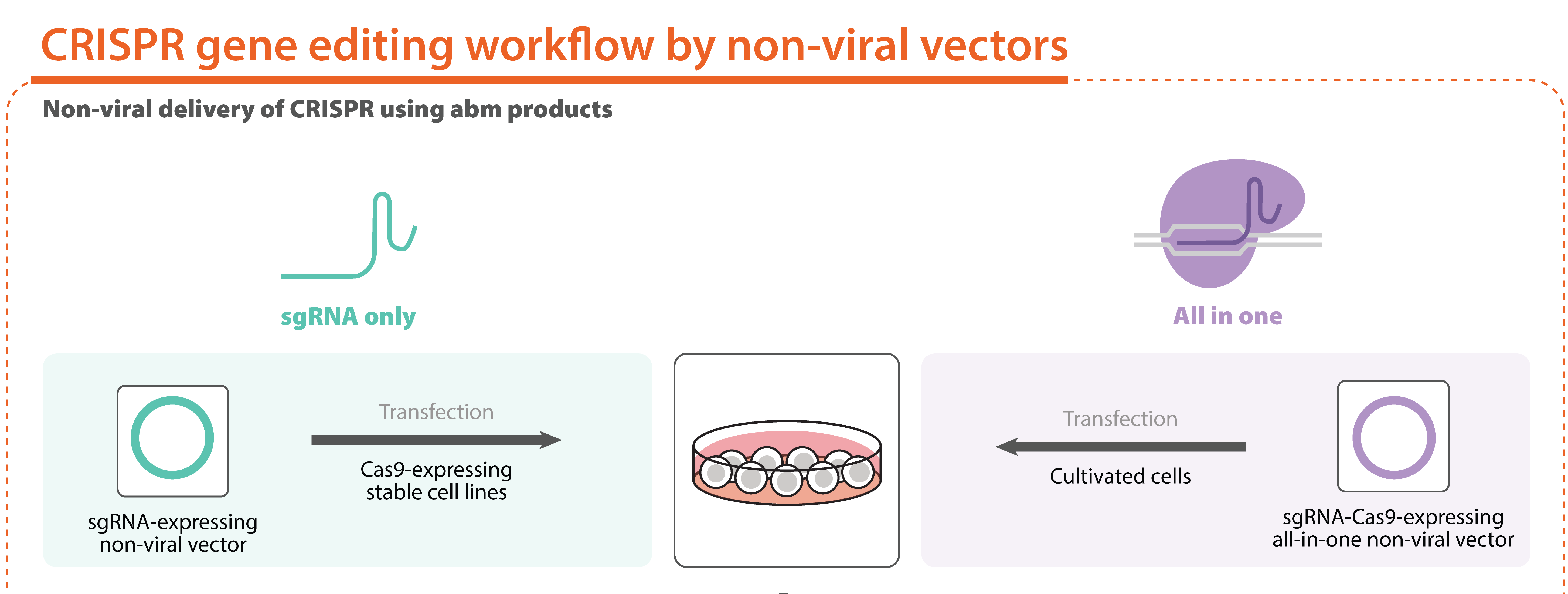
abm's CRISPR Gene Knockout sgRNA Non-Viral Vectors are highly effective at achieving knockout of your target gene. Cas9 functions to create a double-stranded break within an early exon triggering repair via Non-Homologous End-Joining (NHEJ) mechanism resulting in deleterious frameshift mutations. We offer a comprehensive collection of All-in-One (spCas9 and sgRNA expressing) and sgRNA only expressing constructs targeting any human, mouse, or rat gene. Simply input your target gene or accession number into the search bar below.
Key Features
- Comprehensive collection of gene knockout sgRNAs
- Targets include all coding human, mouse and rat genes
- Available in All-in-One or sgRNA only constructs
- Available in a set of 3 sgRNA vectors/viruses for added assurance of successful gene knockout
- Non-viral vector delivery allows for ease of use and high levels of transient expression
Looking for constructs expressing multiple sgRNAs? Check out our Custom Multiplex sgRNA Service.
Popular Products
- DNAfectin™ Plus Transfection Reagent
- Screen It™ CRISPR Cas9 Cleavage Detection Kit
- Custom CRISPR sgRNA Non-Viral Vectors
- CRISPR Scrambled Controls
Search Gene Knockout sgRNA Non-Viral Library
Knockout sgRNA Non-Viral Library
We offer All-in-One and sgRNA only vectors for knockout of any human, mouse, or rat gene.
Can’t find what you’re looking for? Request a custom CRISPR sgRNA Non-Viral vector with technical@abmgood.com.
Additional Information
Documents
Top Publications
Regulation of NKT cell-mediated immune responses to tumours and liver inflammation by mitochondrial PGAM5-Drp1 signalling.
Kang, Y J et al.
Nat. Commun. 6:8371 (2015).
DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9371.
NSAIDs Induce Proline Dehydrogenase/Proline Oxidase-Dependent and Independent Apoptosis in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells.
Kazberuk, A. et al.
Int J Mol Sci. (2022).
doi: 10.3390/ijms23073813
Clinical significance of SNORA42 as an oncogene and a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer.
Okugawa, Y et al.
Gut (2015)
doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309359